Salesforce REST API: How to Expose Apex Classes as REST API Endpoint - POST
Looking for Salesforce Training & HandsOn Projects?
Trailblazer Profile | LinkedIn | Salesforce Blog | Facebook | Youtube Channel | WhatsApp Community
This article is in continuation of my previous
article How
to Expose Apex Classes as REST Web Services - GET Operations where I have explained how to implement a GET
Operation.
In
this article, we will look into the detailed implementation of exposing Apex
class as REST Web Service offering a POST operation to delete records from
Salesforce Object(s).
To
start with the demo, I have set up some of the data in Accounts Object
(Standard Object) which has Invoices Record as its Child
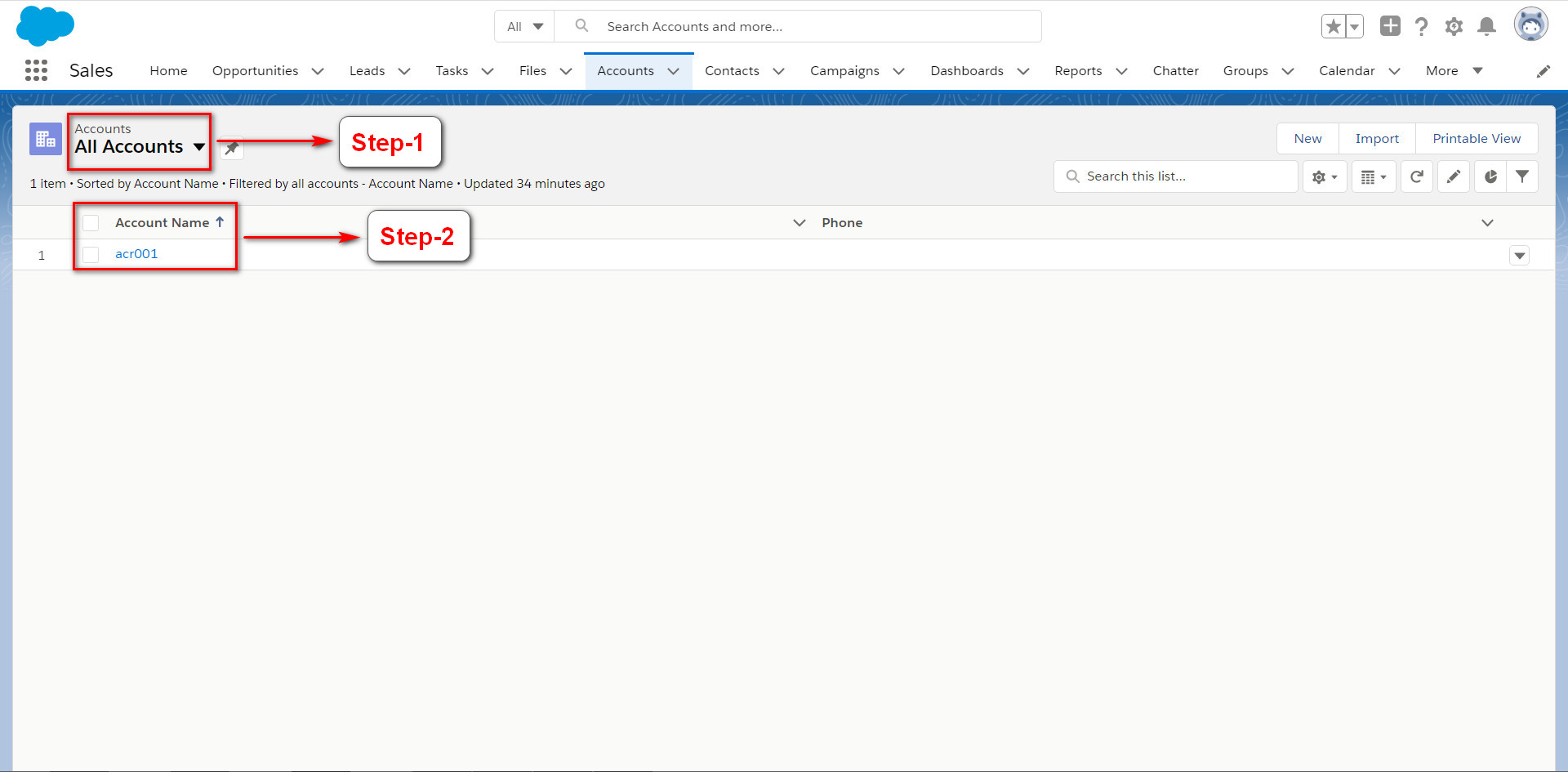
Step-1
& 2: I
have added an Account “acr001” in Accounts Object
Step-5 & 6: If we click any of the Invoice Records, we can
see the respective details. We have a couple of important fields “Invoice Number”, “Invoice Date”, “Amount” to focus on
Step-7: We can make use of the same
“CustomerServices.cls” apex class that we have added in the previous
article
Step-8: Since this is going to be a POST Operation we
should decorate it with @HttpPost method annotations
Step-9: As explained earlier, this method should be “global static” and
it is having an input parameter “customerId” which is nothing but the Account Id
Step-10: RestContext class offers functions that can be used to get
a handle on incoming HTTP Request
Step-11: Since we are passing Account ID as part of
Request URI, we can retrieve & used it as required
Step-12: We are using that incoming Account Id to
search Salesforce Records using SOQL
Step-13: Based on the data returned by the SOQL, we can
build a data collection. This can be done by initiating an entity as shown in
the screenshot
Step-14: Assign “AccountId” to
collections’ “CustomerId” property
Step-15: Assign collections’ “Deleted_Invoice_Details” property to the result set of SOQL query which
is querying “list of
Invoices records” based
on the “AccountId”
Step-16: Assign “IsSuccess” property
to a Boolean value (in Prod version, this should be set based on SOQL DML
Operation outcome)
Step-17: Execute Delete Operation using “Deleted_Invoice_Details” property (which is a list of all invoices for
a particular customer)
Step-18: Lastly we can return entity “delInvoices” as part of the response to this Http Request
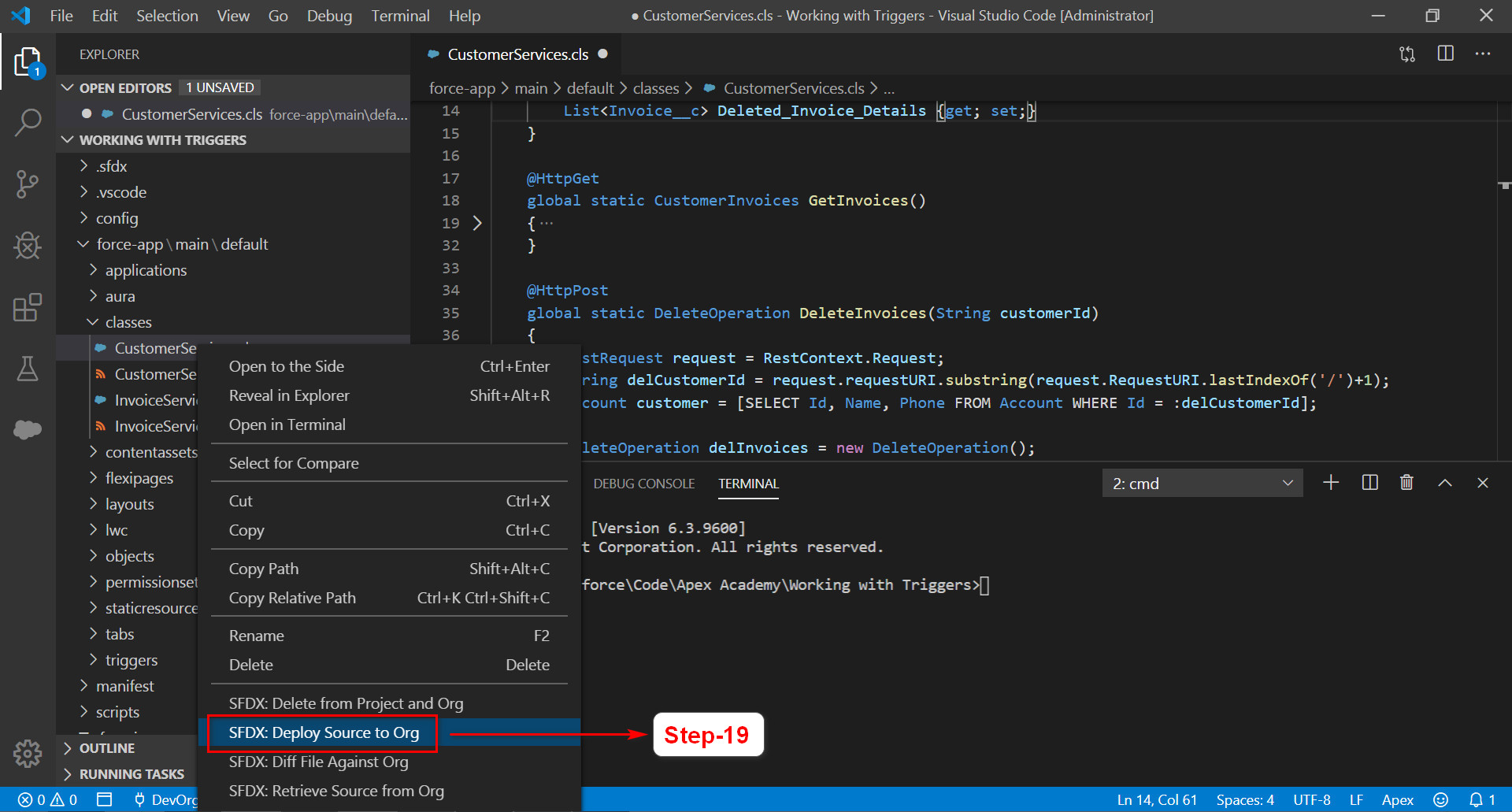
Step-20: We can see the deployment completed
successfully. We can also notice the list of files deployed to Source Org by
looking at the Output window as shown
With this, we have all the code that we need to make
this REST Service functional to handle a delete request (POST).
To
test this web service we can use Postman Web Client. Let’s launch it and see
some action.
Step-21: Since we have defined the Apex function with @HttpPost annotation,
so we need to choose “POST” as the HTTP Request method
We
can define the Apex based REST Service Endpoint Url as per the following pattern
https://<SF
Instance Host Header>/services/apexrest/CustomerServices/<Account Id>
Add the “Authorization” Header and specify its value as “Bearer
<Security Token Received>”. To know about getting Security Token, you can
refer to my earlier article Salesforce
REST API Authentication: The Login Request
Step-22: We should pass a valid JSON as Request Body to
this request definition. This implementation opens up the world of choices for
developers to pass any valid data structure to the API EndPoint
Once the response is received, we can analyze the
response carefully to find the important data points
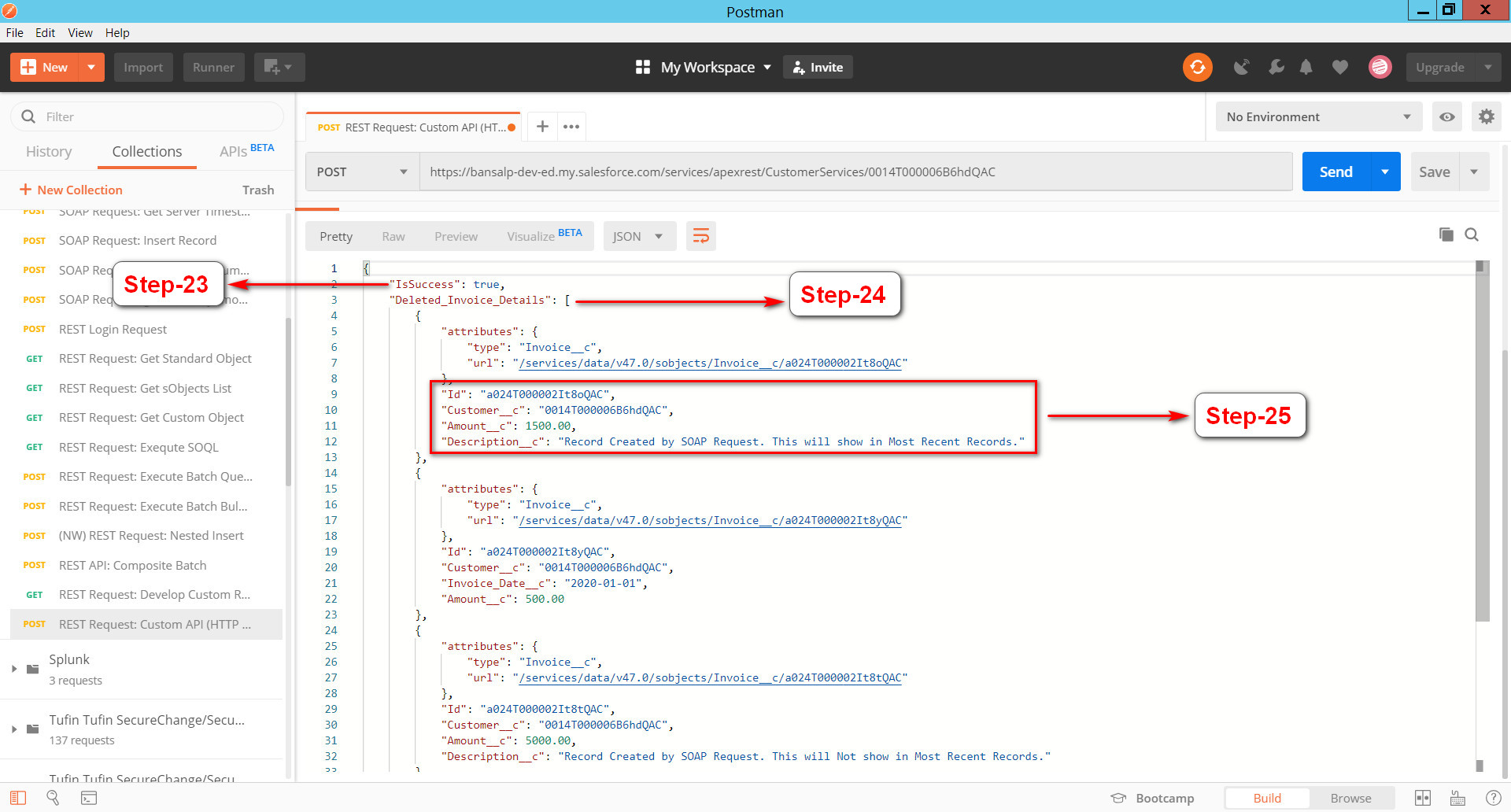
Step-23: Note “IsSuccess” property
returns back as part of the response and this is the same property that we set
earlier in the Apex Class
Step-24: Now note the “Deleted_Invoice_Details” property which
is the list of all Invoices that has been deleted as part of this request
Step-25: Also we can see the details for each Invoice that was deleted. This API response contains
the data structure which is strictly controlled by the API definition we have
exposed as Apex Class
Step-26: Response also contains the “CustomerId” property
that holds the AccountId to which the deleted set of invoices belongs to
Step-27: We can verify if the Invoices are deleted
successfully by filtering the data view as shown
Conclusion
Exposing Apex classes as REST Web Service is a very
powerful implementation around Salesforce REST API Framework. We can leverage
to implement native Web Service Callouts for external applications supporting
integration Use Cases.
- Calls to Apex REST classes count
against the organization's API governor limits.
- The maximum request or response size is 6 MB for synchronous
Apex or 12 MB for asynchronous Apex.
- Apex REST supports OAuth 2.0,
Session ID authentication mechanisms









Comments
Post a Comment